Q. What is cloud computing? I am a Non-IT person and have no clues about cloud computing.
Ans: As per the wikipedia definition, “Cloud computing is the delivery of services of the computing a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software, and information are provided to computersand other devices as a utility (like the electricity grid) over a network (typically the Internet). Clouds can be classified as public, private or hybrid“.
Sounds too long definition to understand? Lets start with the understanding the source of IT resources like computer, storage and network. Its called Datacenter which is a dedicated secured and highly available IT Site/Sites/Rooms/Rooms with temperature control and required heat flow, having bunch of running computers/servers stacked together in racks, connected using networking and storage components and to achieve specific business needs using business driven applications installed on these servers.
Traditionally, when a requirement for compute resource would arise, end user had no or very minimal control over procuring required resources. The requirement had to go via approval process to the systems administrators and followed through procurement and build process and once built with required storage, network and security requirements hand over to the end user for application deployment. This had challenge due to lead time of procurement and build process ( sometimes 1-2 months ).
Lets understand other challenges in building new or manage existing Datacenter with no cloud model in place.
- Need floor space for setting up small/mid or large scale datacenter
- Manage cost of all Datacenter requirements ( like power, cooling, racks, cabling, servers, storage, networking devices etc )
- Manage and day to day operational support expenses for datacenter operation
- Manage vendor support and license costs
- Manage cost of provisioning, decommissioning, monitoring and backup solutions.
- Manage security, vulnerability scan, antivirus products and support cost
- Manage the cost of PCs/Computers/Storage/Servers and Networking based software products and licensing.
- Manage expenses on Operating System, Database and Application development or proprietary software
- Manage infrastructure tiers as a part of product development cycle ( Dev, Test, UAT, Pre Prod, Prod )
- Buy additional capacity for setting up Disaster Recovery solutions.
- For redundant and scalable infrastructure, will need purchase additional hardware ( like CPU, Memory, HDD, I/O PCI cards etc), allow downtime of your running system (server, computer) and then fix it ( only if you know how to add otherwise pay to the respective vendor to get this done).
- Time consuming server provisioning processes ( Plan, Order, Approval, Availability Lead time and then delivery ).
- Unable to seamless scale up or scale down as per the requirements
- Once hardware is bought will be up and running till the end of life whether not or partially used. That mean wastage of floor space, power, cooling and rack space size.
- Another big challenge comes from old legacy hardware, which are not under support. It costs much more to support EOL hardware than buying new one.
- Availability comes as biggest challenge in maintaining datacenter with no cloud functionality
Now on top of above challenges, think of a business case where client is a startup business or small ISV, is setting up a new business and not sure about the long term impact on such investments, above expenses may turn to be a complete disaster.
Instead what if all Infrastructure components like Servers, Storage, Network, Application offered to the clients as hosted services? Like you provide a web/app based portal to end user to define their requirements, and once they submit the requirement form, the required host/storage/application/database or network bundled services setup and started as expected. Also, as per their needs end user would like to see further flexibility on
- Easy scaling of computing resource needs ( scale up or down )
- Elastic in nature
- Should be charged as per the services bought
- Should be highly available
- Should be monitored
- Should be automated as a part of managed services
- Should be able to decommission anytime with no extra hassle.
To address above solution is a cloud model. So basically you think of Cloud as a
- Managed virtual computer (instances), which is served as “on-demand” and easy and quick provisioning
- Offered as “Pay as you use” model ( Public ) or Charge back model ( Private cloud )
- Automation for provisioning, modifying, decommissioning, backup, high availability, monitoring
- Independently priced computing resources ( like CPU, Memory, Storage, Networking, Software,Application etc )
- Can be easily expanded or reduced ( elasticity)
- No infrastructure management and operations support cost ( In case of Public Cloud)
- Provides disaster recovery and backup offerings these virtual hosts ( with minimum downtime )
- Accessible to from anywhere. ( Public Cloud )
- Third party managed infrastructure services ( Public Cloud )
Q. What are different types of cloud computing solutions
Ans: Cloud computing are commonly defined as below types
- Infrastructure as a service (IAAS)
- Platform as a service (PAAS) and
- Software as a service (SAAS)
Although some new definitions on the cloud computing models are also coming up as Storage as a service, Network as a service, Database as a service, Desktop as a service etc.
Q. What are different models of cloud computing ?
Ans: Cloud computing can be adopted for Private, Public or Hybrid model.
Private cloud computing is mostly adopted by organization restricted by compliance and regulatory governance. In private cloud, company still owns and manages the back-end infrastructure but utilize them optimally by adopting cloud methodology and reducing time to provision a cloud service and other cloud offerings.
For Public Cloud Computing, the infrastructure services are accessed via internet based cloud hosting providers and charged on “Pay as you” model with different resource models. Public cloud computing is commonly used by non business critical or small and medium size business.
Hybrid Cloud Computing is something which is hybrid model of Public and Private cloud solutions. Mostly adopted Cloud model is used by Enterprises to bring IT Infrastructure under cloud control, mixed with critical and non critical business requirements..
Q. Can I fulfill all IT requirements public cloud based solutions rather than setting up local IT Infrastructure?
Ans. This is something, that requires further consulting to understand what your business priorities are. If your priorities are to reduce the TCO of your company IT spend, reduce of pain of company managed Infrastructure operation and support and compliance and governance ( specially adhering to shared platform model) are not in priority list then Public Cloud Computing can certainly help you define a model which allows you to reduce the total cost of ownership (TCO) of your IT Infrastructure. For example you are a Start Up , and need computing resources as playground areas to try and test the product you plan to launch. So instead of buying servers/desktops and setting up your own IT Infrastructure/Datacenter, you rather go for cloud based infrastructure and other software services, use them, if it all goes well, carry on further with services otherwise you can stop services. For more detailed consulting for specific requirements send your request for consultation by clicking on Contact .
Q. What are the benefits of using cloud computing in my IT Infrastructure?
Depending upon the type of cloud computing solution ( Public, Private or Hybrid ), cloud computing comes as larger plus as against having own Datacenter or Managed services. Below are the list of Cloud Computing based solutions.
- First and foremost reduced cost is one of the most important benefit. Cloud model allow customer to buy or stop infrastructure services as and when needed as “Pay per use”.
- Cloud solution provides scalability of computing resources. They are elastic in nature, which means, as and when needed resources can be added or reduced.
- Multi-tenancy , in terms of capability of having multiple operating system based Infrastructure is another advantage.
- Reduced time to provision an Infrastructure. Where provisioning of a server may take 3-4 weeks of time starting from procurement of hardware to racking, patching, networking, storage allocation to host build process, cloud instance can be provisioned in minutes with the click of few buttons.
- No Infrastructure operational and support costs
- And accessible from anywhere as this is completely internet based service.
Q. Are there challenges using cloud computing?
Ans: Yes there are, but not for every situation. Some common challenges are
- Due to shared services, or multi tenancy nature of cloud, if your data need to adhere to certain compliance or local governing standards, then cloud solution could be challenging
- The other challenge is Data security. Although now a days most of the cloud provider are providing additional level of security with add on Firewall and VPN based services, still there are challenges to Data Encryption or Data communication from Client to the cloud providers.
- Another challenge is the complete control of Datacenter Infrastructure lying with vendor. First is you are locked to the Infrastructure services and offerings provided by the vendor.
- SLA and KPA should be carefully and clearly stated and defined for cloud services, like in case of unavailability of services or data breach as a part of contract of agreements.
- For some customer data location matters ( although this is against cloud computing principles ). Local governance is one of such example, which restrict data residing on other geographical location than permitted.
- Although cloud computing is meant to reduce the cost of ownership of IT Infrastructure, this cloud be challenging and need due diligence to analyze the effective cost benefits by cloud or migrating existing Infrastructure to cloud model. Remember cloud model is “Pay as you” for every infrastructure and software services, so you spend hourly, daily, monthly or yearly basis ( based on the contract with cloud provider) for every bit of service ( CPU, Memory, Storage, Network, Disk, OS, VPN, Firewalls, DR, Monitoring, Backup).
- Other aspects of cost of ownership of cloud model is like to increase due to charge back model. If this model is not carefully implemented, there are likely chances of overhead of cost.
- Some compliance demand Datacenter audit reports and as the entire control of Datacenter lies with the service provider, this could a big challenge if there is a breach of compliance.
- In a cloud model for IAAS based cloud computing, unit of CPU is measured as vCPU, which is a fraction of core or a full core. So the challenging part is none of the public cloud provider provide CPU speed . This is mainly due to the nature of cloud computing infrastructure, as back-end hardware could be a mix of different CPU blades/servers. Having said that it cloud produce challenges where workload analysis is done based on CPU speed being one of the core factor. Also initial budgeting of Infrastructure compute resource does require matching CPU speed with vendor defined or previously available bench-marking reports. So by not mentioning CPU speed, it will be difficult to understand how many cloud instances or what power should be bought.
- Cloud is not a right choice for high computing based workloads or in other words, vertically scaling up requirements. Cloud solutions are best suited for horizontally scale compute resources.
Q. What is the current state of Cloud Computing in India?
Ans. India is definitely a growing business and there are plenty of opportunities in India. As per the report published by Gartner estimates that in India alone the market for cloud-based services will rise by a third to $557 million this year, and more than triple by 2018. Having said that so far only 2-5% of total IT Infrastructure is under cloud infrastructure.
Q. Which is the right kind cloud computing model out of Public, Private or Hybrid for our organization?
Ans: There is no straight answer to this. This will need a detailed consulting engagement to understand different business needs and accordingly align them to different models of cloud computing. Non business critical environments are the first and easy target to move to Public cloud. Although Production/Live environment can also move to cloud model, as far as they are not breaching agreed compliances. If there is a restrictions due to geographical based data compliance, then Private cloud will be a better choice. Most of the organization though choose to have Hybrid cloud model, which allows them to avail balanced use of both cloud computing solutions.
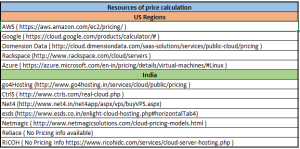
Q. Any information of cloud providers in India?
Ans. There are plenty of cloud provider in India.
Below is the list of some well known India hosted cloud solutions providers
CtrlS, BSNL, Tata Telecommunications, IBM India, Net4, Reliance, Salesforce India, Netmagic, Go4Hosting, Mictonova, Rioch, WebWerks.
Additionally, other internationally known cloud solutions provider
Amazone (AWS), Dimension Data, Salesforce, Rackspace, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Apple Cloud Storage etc.
For further comparative study based consulting on these cloud providers, connect via clicking Contact .